galvanic corrosion...? galvanic isolation...?
let's make it simple!
All metals have a “natural” electrical charge . Different metals have different electrical charges. The bronze propeller has a different electrical charge (voltage) to the stainless steel propeller shaft. The rudder has a different natural voltage to the metal hull. If we were to place the bronze prop and the stainless shaft into the water without connecting them physically together there is no problem. Both the metals remain in their original state. If however the propeller is physically connected to the shaft and we place them in water things begin to happen! The metal with the highest natural voltage will try to discharge its voltage to the other metal. When electrical current flows between the two metals (via the water) corrosion will take place. The metal with the lowest natural voltage will be fine but the metal with the higher natural voltage will corrode....bad news! We overcome this problem by attaching an additional metal to the propeller shaft. This chosen metal has an even higher natural voltage than the bronze prop or the steel shaft. This metal is known as the “anode”. We now have 3 metals connected together in the water. Current will always flow from the highest voltage to the lower voltages and the “anode” (highest voltage) will corrode and reduce in size, over time disappearing completely.
The good news is the other two metals remain intact. By “adding” the anode we have protected the valuable shaft, propeller and all other metals below the waterline . When the anode finally corrodes away the next “highest” voltage metal (the bronze prop) will begin to corrode. It is essential that anodes are inspected regularly to ensure they are capable of protecting all the other underwater metal fittings. When the anodes have gone so has your protection! So far so good! Providing our anodes are good, well connected and of the correct size and type we can minimize corrosion of our underwater connected metals.
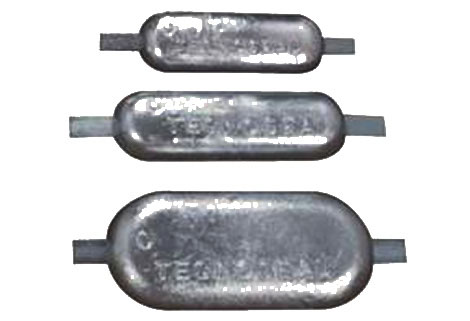
By adding an anode(or multiple anodes) we can protect all the other metals. The anode will eventually corrode away.
When this happens the other metals will corrode.
Obviously we need to regularly check the condition of the anodes.
When the anodes have gone so has our protection!
So far so good. Providing our anodes are good, well connected and correct size and type we can minimise corrosion of our underwater connected metals No need to worry then? Not quite! Let’s look what happens when we plug into marina shore power electricity.
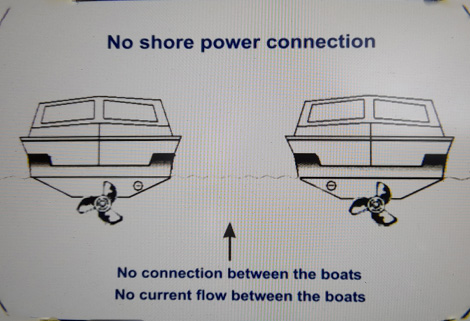
We moor our boats alongside other boats, metal pontoons and metal stanchions. Boats have lots of metals all in the water. Metal hulls, metal propellers, drive shafts, outdrives, skin fittings, trimtabs, rudders etc. We have protected the metals on our boat by fitting sacrificial anodes which in turn are connected to all our underwater fittings. We are not physically connected to our neighbours boat we are separated by the water. Our neighbours boat cannot affect us... Or can they?
It’s cold outside. The batteries are going flat. We need a brew! We need electricity! Here comes the mains! When you plug into mains shore power the cable you use has three internal cables: A live, a neutral & an earth wire. The earth wire goes to the shore power pedestal where it is physically connected to the ground. This is a safety wire and protects you in the case of an electrical problem. Your neighbouring boats also use the same earth connection. This effectively connects all the boats together via the earth cables in the shore power leads. In your boat the shore power earth lead goes to your electrical consumer unit & then to all metal components such as the engine block, fuel tanks, shafts / propellers etc & then finally connects to your anodes. Unfortunately as all the boats (and metal pontoons) are now interconnected via the earth cables any voltage leaks or "galvanically" generated voltages have an easy path between the boats. This often results in rapid loss of sacrificial anodes & increased corrosion of all underwater metals. If the boat next to you does not have anodes he won't worry: He is using yours!
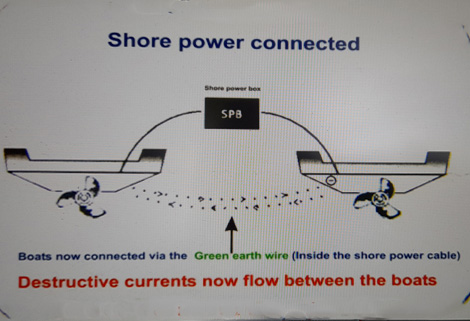
A galvanic isolator does not replace your sacrificial anodes which are essential to protect your underwater metals. It is used in conjunction with the anodes to control additional corrosion paths experienced when connected to shore power. A galvanic isolator does offer protection from both stray currents & galvanic currents which attack your boat via the shore power earth cable. These currents can transmit from other boats, metal pontoons & leaks on the 240 volt systems in the marina. Serious leaks can devastate your props / shafts/ anodes etc in a matter of weeks. Surveyors & boat inspectors will usually recommend fitting a galvanic isolator in the marina environment (They see the effects of unprotected boats all too often).
How do I fit a galvanic isolator?
Isolators are easily fitted between the shore power inlet of the boat and the consumer / distribution panel onboard.
If fitting internally the isolator is fitted in the earth circuit by cutting the green/yellow earth cable and inserting the isolator between the two points.
Isolators are also available for external connection either on the pontoon or on the boat. These easy fit isolators simply plug into the shore power cable and can be installed in under 30 seconds!
Further information or free information pack:
www.safeshoremarine.com or Tel 01977 513 607

Over 24,000 UK boats are now protected by Safeshore galvanic isolators! 20 years of professional service.
Tried, trusted, reliable quality with lifetime warranty.
Safeshore supply isolators for every vessel... D.I.Y. internal fitting or easy fit plug-in units, offering maximum protection, total reliability and superb customer service.
Guaranteed protection from both galvanic and highly destructive stray current corrosion.
Call: 01977 513 607; Write: email Visit: website
